Parts Implemented by Furkan Akgün¶
Change Log¶
We created log class to be able to track user activities and also debug the site when a problem occurs. Log class simply consists of three major columns excluding id; first is the description and generated right after an operation is performed, second is the user logged in when given operation performed , this way we are able to track any user activites, and finally third one is the date of operation.
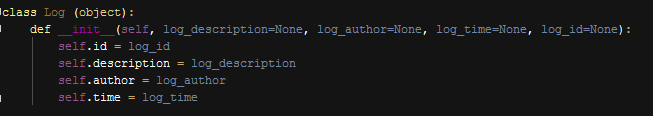
Log Properties
Inside log class, we have three functions; retrieve a log by passing an id or retrieve all without passing an id, adding log data to database and deleting log data from the database. Now we will cover these three functions respectively.
Adding a Log to the Database¶
To be able to show logs in home screen or manager main screen we needed to add them to the database. To add log data to the database, we simply created an object and then set its properties. After an instance of object have all properties set, we simply call add_to_db() function. This function basically use insert query, the variables in query are the properties of this log instance.
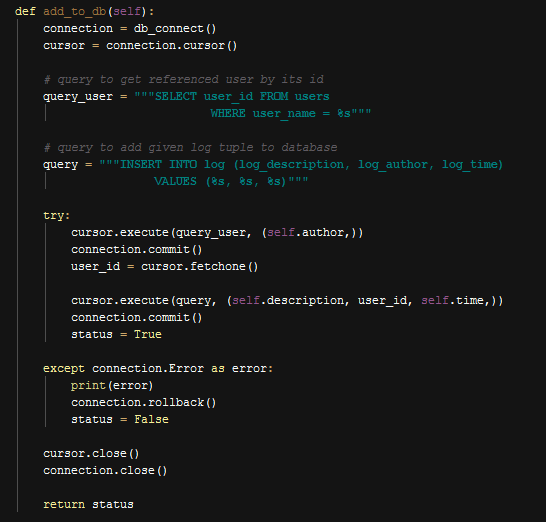
Function to Add Logs to Database
In log class, one of the properties was user or author and it is a foreign key to the user table. But we were setting author or user by its name, so to get user’s id with that name we needed to run a query first to find user id.
If instance of log class have all properties set to appropriate values then the function will add log to the database.
Getting Log(s)¶
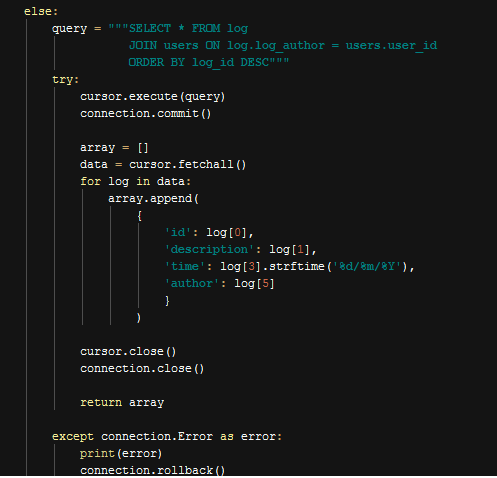
To show all logs or some logs in the front view, we needed a function to return all log data or just a single one with given id. get_log_by_id(get_id) function simply takes an id parameter; if the id is none (or no parameter entered), the query will be executed with no specific id parameter and all logs will be returned from query and all will be stored in an array. Thne the function will just simply return that array.
Function to Retrieve All Logs
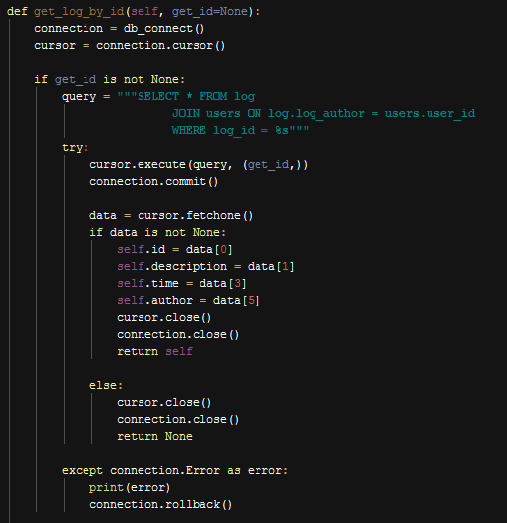
On the other hand if an id value is entered as a parameter, then the query will be executed with “WHERE id=get_id” and only the log with specific id will be returned.
Function to Retrieve A Log
Deleting a Log¶
Deleting a log is not implemented in front view, but is ready in class as a function. Simply we get referenced instance of log and then call delete_from_db() function.
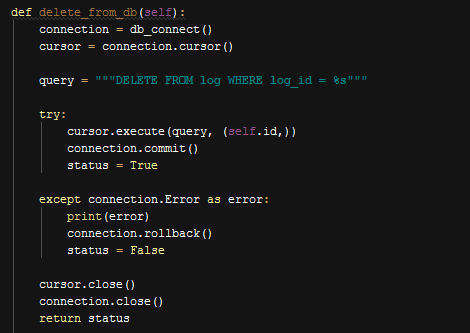
Function to Delete a Log From the Database
Creating Logs After an Operation¶
Logs are instantly created when user performs an operation in the database. It is generic in all parts of operations, a description is created right after the operation and a log instance is created with this description, user and date. After that add_to_db() function on that log instance is called and log is added to the database.
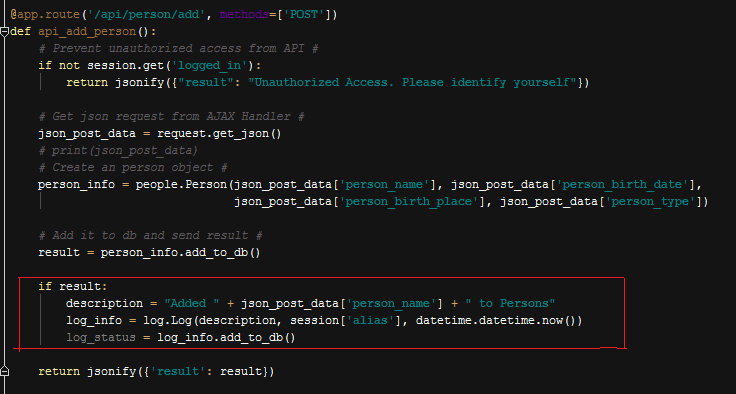
Generating a Log After an Operation
As you can see right before function is completed a description is created given the operation. Simply “Added”, “Updated” or “Deleted” expressions are used for all operations. Here user is passed to the object constructor as session[‘alias’].
Displaying Last 5 Changes in Home Page¶
After we have a function to get all logs, it was too easy to select only last five of logs sorted by date. In query of selecting all logs we did already sorted logs in descended by date column. So it is now reduced only to chose first five rows returned from SELECT statement.
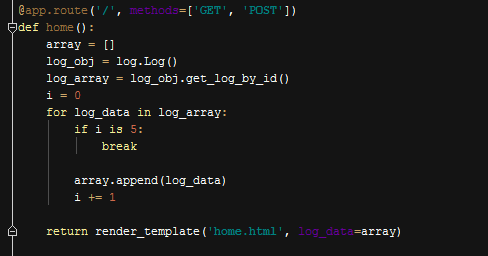
Choosing Last Five Changes
Only five log data are stored in array, and then array is sent to the home page. In home page we can now simply display them with a for loop.
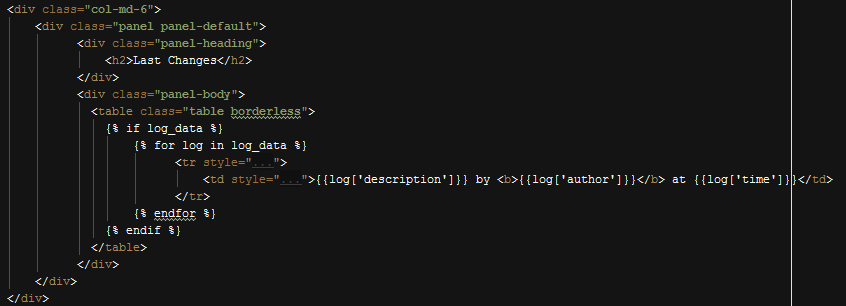
Displaying Last Five Changes
Displaying All Changes in Manager Main Page¶
Just like displaying last five logs, but now there is no need to use a constraint. We simply retrieve all data and store them in an array. Then send the array to manager main page as data.
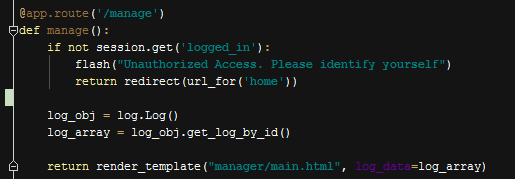
Choose All Logs
Then simply display each of them by a for loop.
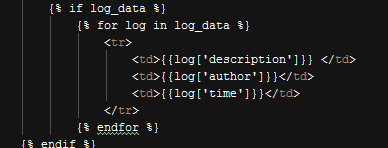
Displaying All Logs
Generic Function Bodies¶
All classes have same function bodies. They differ with only the queries they have. So to reduce explanation for each of them, I will show generic function bodies.
First is add_to_db() Function,
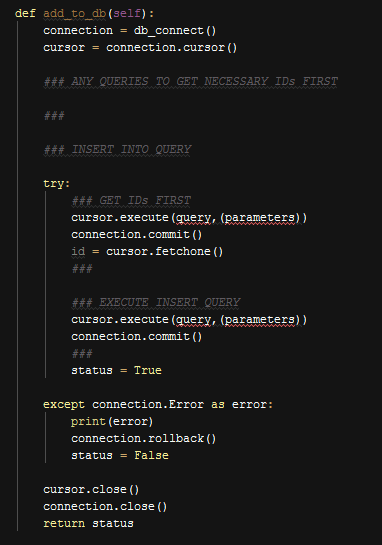
Generic Add Function
All classes share these bodies, only difference is queries. Another thing is just like in the above example some class properties are set with name values but we instead use id values for them. So first we must call another queries to get their ids. Then simply execute operational query.
update_db() Function,
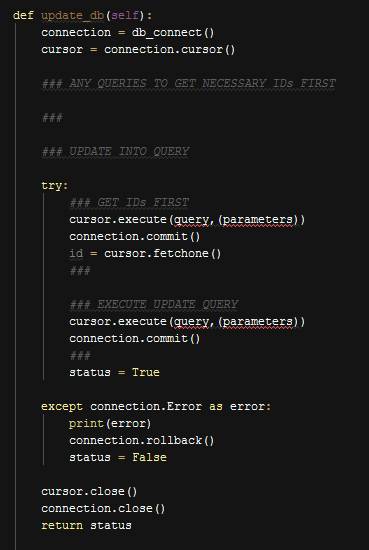
Generic Update Function
delete_from_db() Function,
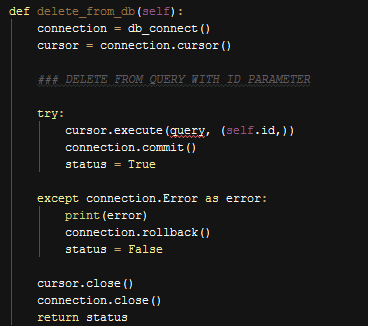
Generic Delete Function
get_(classname)_by_id() Function,
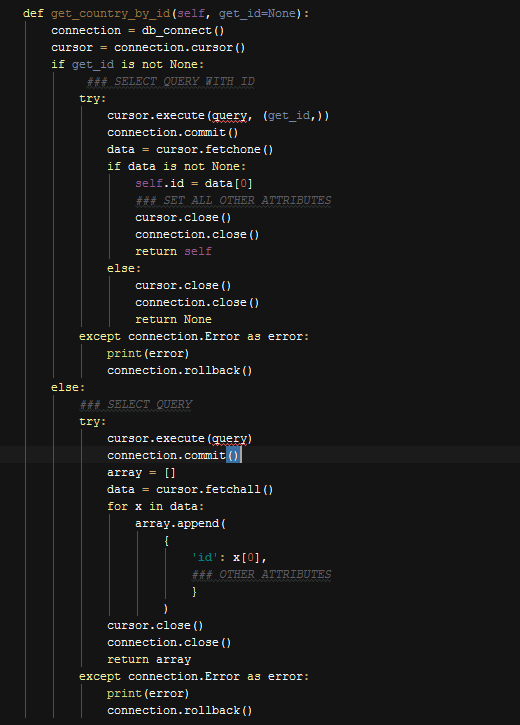
Generic Retrieve
Functions up to now were only class operations. Each class have four functions above. Next functions are for add, delete, and update operations done in website. These operation are again same for other classes except some extra operations for getting referenced objects.
Add Operation,
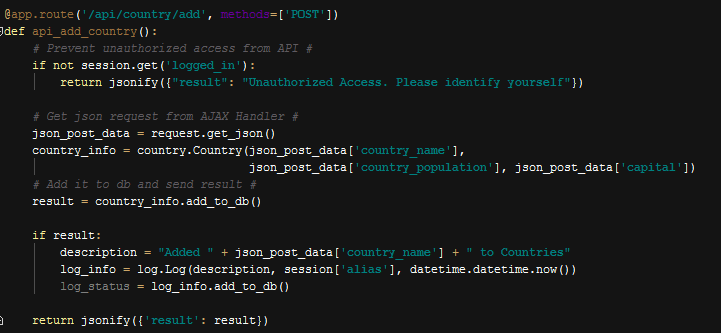
Generic Add Operation
As can be seen above, add operation creates an instance of class with json data provided by forms. After an instance is created that objects is added to the database. After a log will created for this given operation and the operation ends.
Delete Operation,
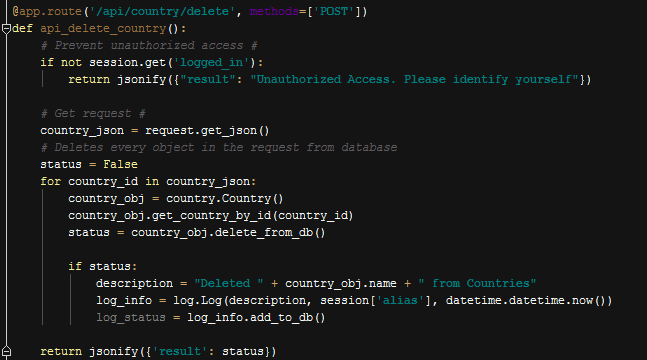
Generic Delete Operation
In delete operation we get all selected item ids in an array, then in a for loop we delete all selected items.
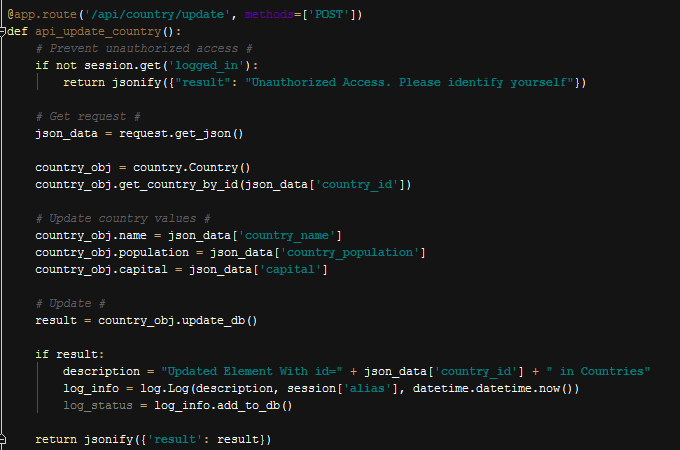
Update Operation,
Generic Update Operation
Just like in the add operation we get json data from forms and instead creating a new entry, we set properties of this instance to what we get from the forms and then update the item.
Country¶
Country object has four properties; id, name, capital and population. Capital is a foreign key to the cities table.
INSERT INTO QUERY¶
We have already provided bodies of all the functions. Those bodies were all same for all classes. What makes each class different are their unique queries for operations. These queries are executed in those functions and we complete what we try to accomplish.
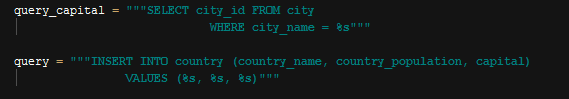
Country Insert Into Query
In above queries, first is used to get id of the referenced capital, and then all properties of class are used as parameters to add this instance to the database.
SELECT QUERY¶
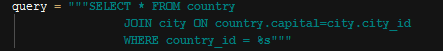
Country Select Query
In case we pass no parameter to get_country_by_id() function, the query with no “WHERE” clause will be used. Above query is used when we pass an id parameter.
UPDATE QUERY¶
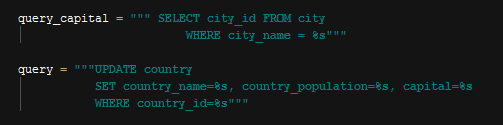
Country Update Query
Just like in the add operation queries excluding update query gets referenced item ids and then use them as parameter in the update query.
Matches¶
Match object has nine properties; id, home team, score of home team, away team, score of away team, stadium, referee, league and match date. Team, stadium, referee and league are all foreign keys.
INSERT INTO QUERY¶
We have already provided bodies of all the functions. Those bodies were all same for all classes. What makes each class different are their unique queries for operations. These queries are executed in those functions and we complete what we try to accomplish.
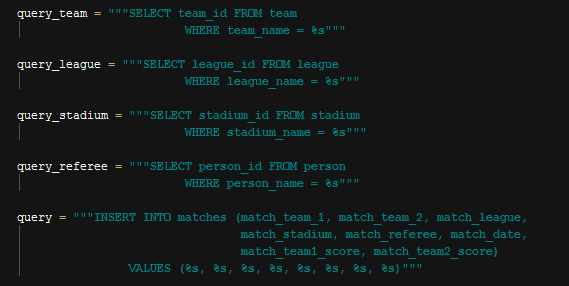
Match Insert Into Query
In above queries, queries except the last one are used to get ids of the referenced items, and then all properties of class are used as parameters to add this instance to the database.
SELECT QUERY¶
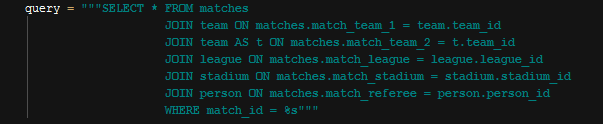
Match Select Query
In case we pass no parameter to get_match_by_id() function, the query with no “WHERE” clause will be used. Above query is used when we pass an id parameter.
UPDATE QUERY¶
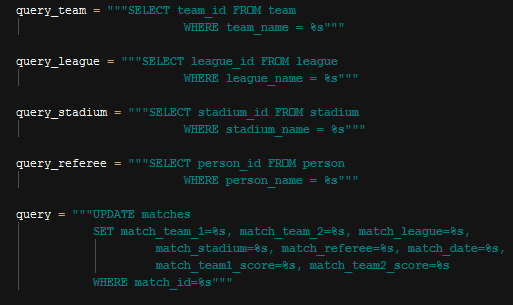
Match Update Query
Just like in the add operation queries excluding update query gets referenced item ids and then use them as parameter in the update query.
League¶
League object has four properties; id, name, country and start date. Country is a foreign key to the country table.
INSERT INTO QUERY¶
We have already provided bodies of all the functions. Those bodies were all same for all classes. What makes each class different are their unique queries for operations. These queries are executed in those functions and we complete what we try to accomplish.
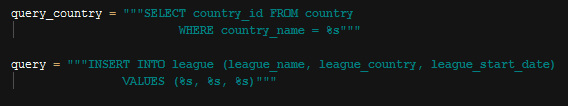
League Insert Into Query
In above queries, first is used to get id of the referenced country, and then all properties of class are used as parameters to add this instance to the database.
SELECT QUERY¶

League Select Query
In case we pass no parameter to get_league_by_id() function, the query with no “WHERE” clause will be used. Above query is used when we pass an id parameter.
UPDATE QUERY¶
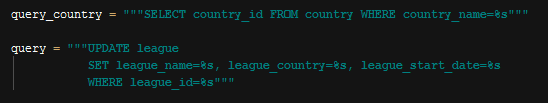
League Update Query
Just like in the add operation queries excluding update query gets referenced item ids and then use them as parameter in the update query.


